Friday, December 15, 2006
Final Document
This is to inform that documentation is available on
www.freewebs.com/ruchiraparihar/graffi-v.exe
which can be downloaded to understand the concept.
Friday, October 27, 2006
Exploration- User Testing Prototype 1
one male and one female to test the working of the prototype
It was quite an interesting experience to watch them interact with the system
The video of prototype 1 is uploaded at www.freewebs.com/ruchiraparihar/proto_upload.htm
www.freewebs.com/ruchiraparihar/proto_test1.htm
Exploration - White Paper ( Final Stage)
There were big white sheets being stuck in three computer laboratories where students work for almost 24 hours
The three laboratories differed in the following terms:
IT Lab had 24 students , 1 paper and no writing instrument provided
New MediaLab 8 Students, 1 paper and a sketch pen as a writing instrument provided
SUID Lab 5 Students , 1 paper and no writing instrument was provided
The project carried on for 4 days.
here are the images at
the first stage:
the intermediate stage:

the final stage:

The observations and deductions were:
For such a thing to take place, the instrument with which they write is a major factor which holds them from writing, i.e. if people don’t have a pen in their hand ( or in the vicinity ) they wont attempt to write even if they have something to write
The above point makes it clear that users would be happy to use voice as a tool to make graffiti because, they wont have to wait for an instrument to be in their hands, all they need is their voice.
Very few people take the initiative to be the first ones to write, i.e. the initialization should be done already for people to carry on the chain reaction.
Hence, the system of Graffi-V should be such that it initiates graffiti on its own and is exciting enough to invite people.It can do things like generating a random quote on its own, or start saying something like "who is it?" , and there can be people answering to the questions being put up and there will be graffiti in response to whatever they would say.
Usual scribbles on the white paper are often answering the one who has written before them.
It is interesting to note an answer back pattern.
Which gives an idea of a chat based interface, where two people talk and they create graffiti.
People use it as a messege board to leave messeges for all.
Hence the idea of a messege board, or a thought for the day board.
People crib a lot when given a chance to write on the paper, and when their identity is not revealed.I found obscene stuff on one of the whitepapers.
Hence there should be word filters if such a system is to made public.
Also , it can be used as a place to vent out one's frustrations.
I also found reminders on the whitepaper.
Hence it can be used as a reminder board.
It can also be used to save stories ( as in saving the memories for the others to scroll back and see )
I realized that the three labs were differing in their scenarios, it makes clear that the more the number of people involved , the more is the fun and more is the involvement in turn.
Research- Human Factors in Speech
Human factors in speech
?>?>?>?>
For many years a group of human factors specialists have studied the implications of speech technology on human computer interaction.
In addition to physiological aspects of human factors, there are the cognitive and psychological aspects of human interacting with speech technology in computers .for example what constraints must users observe in their speech so that a speech recognizer can understand them?
Does constraining their speech make them more or less effective? Does it change the way they work? How do people react to synthesized speech? Do they mind if the computer sounds like a computer? Do they prefer that it sound like a human? How does computer speech affect task performance? Now add this to the aspect of Multi-Modality. Some speech technology involves speech only, but a significant portion of the interfaces being designed with speech are multi-modal. They involve not just speech, but other modes such as tactile or visual. For example a desktop dictation system involves speaking to the computer and possibly using the mouse and keyboard to make corrections. Speech added to a personal digital assistant handheld device means that people will be speaking while looking at a small screen while pushing buttons. Research is looking at when people use which modes and how they use them together.
Here, then are some of the human factors issues surrounding speech technology.
High error rates
Neural network technology dramatically improves speech recognition systems and allows speech recognizers to hear human speech even better than humans do, especially when competing with background noise.
Much work has to be done to help humans to detect errors and to devise and carry out error strategies. Imagine if every tenth key press you made on your keyboard resulted in the wrong letter appearing on the screen. This would affect your typing and your performance significantly. That describes the state of errors with speech recognition for many systems.
Unpredictable errors
Besides relatively high error rates, the errors that speech systems make are not necessarily logical or predictable from the human’s point of view. Although some are more understandable- such as hearing ?>?>?>?>
When we speak to a computer we don to appreciate the effect that such qualities as intonation, pitch, volume, and background noise can have. We think we have spoken clearly but we may actually be sending and ambiguous signal. The computer may understand a phrase one time and misunderstand the same phrase another time. Users do not like using un-predictable systems lower interims of acceptance and satisfaction of speech technology
People’s expectations
Humans have high expectations of computers and speech. When they are told that a computer has speech technology built in they often expect that they will have a natural conversation with it. They expect the computer to understand them and they expect to understand the computer. If this human-like conversational expectation is not met (and it is often not met), then they grow frustrated and unwilling to talk to the computer on its realistic terms.
However if humans are given realistic expectations of what the computer can and cant understand .then the are comfortable constraining their speech to certain phrases and commands. This does not seem to impede performance on task. Using constrained speech is not a natural way for people talk to pother people or even a natural way for people to talk to computers .nevertheless, within short time users can learn and adapt well to constrained speech.
Users prefer constrained speech that works to conversational speech those results in errors.
Working multi-modally
Many tasks lend themselves to multi modality for example a traveler may point to two locations on a map saying “how far?”... People will use one modality such as speech alone followed by other another modality such as pointing with a mouse or pen. In other words they will switch between modes. Sometimes they use two or more modes simultaneously or nearly so for example pointing first and then talking.
Speech only systems tax memory
Because a speech only system lacks visual feedback or confirmation, it is taxing on human memory. Long menus in telephony applications for instance are hard to remember
Spoken language is different
People speak differently than they write, and they expect systems that speak to them to use different terminology than what they may read. For example, people can understand terms such as delete or cancel when viewing them as button labels on a GUI screen but they expect to hear a less formal language when they listen to a computer speak
Users are not aware of their speech habits. Many characteristics of human speech are difficult for computers to understand, for example using “ums” or “uhs” in sentences or talking too fast or too softly .Many of these characteristics are unconscious habits.
People Model Speech
Luckily people will easily model another’s speech without realizing it. We can constrain or affect the user’s speech by having the computer speak the way you want the user to speak. People tend to imitate what they hear!
This is taken from the book "Designing Effective Speech Interfaces" by Susan Weinschenk and Dean T Barker
Research- Types of interfaces
We are concerned with how to design products so that people can be productive as possible with the product, as quickly as possible. Designing to optimize usability means paying specific attention to how the interface looks and acts
This includes
¨ Ensuring that the interface matches the way people need or want to accomplish a task
¨ Using the appropriate modality for example visual or voice at appropriate time
¨ Spending adequate design time on the interface
What are the types of interfaces?
There are several types of interfaces.in the past and still around to some extent were character based user interfaces then graphical user interfaces became prevlent and next came web user interfaces WUI and then speech user interfaces
What is speech interface?
It would be simple to answer but it is not
Because it is a relatively new idea to have our technology involve speech. This is a field that is just starting to grow. Like any new field, the definitions and terminologies are not standard
Speech interfaces
The term speech interface describes a software interface that employs wither human speech or simulated human speech. You can further break down interfaces into auditory user interfaces and graphical user interfaces with speech.
Auditory user interfaces AUI
An auditory user interface is an interface which relies primarily or exclusively on audio for interaction including speech and sounds. This means that commands issued by the machine or computer as well as all commands issued by the human to control the machine or computer are executed primarily with speech and sounds. Although AUI may include a hardware component such as a key pad or buttons visual displays are not used for critical information
Examples are
¨ Medical transcription software that allows doctors to dictate medical notes while making rounds
¨ Automobile hands free systems that allow drivers to access travel information and directions
¨ Interactive voice response systems in which users access information by speaking commands such as menu numbers to listen to information of their choice
¨ Products for the visually impaired that rely only on audio text and cues
Graphical user interfaces with speech
AUI where the user interacts with the software primarily via speech.we call these multi-modal interfaces ie graphical user interfaces with speech or S/GUI for speech/GUI
¨ A word processor that allows users to dictate text instead of or in addition to typing it in
¨ Web navigation software that allows users to navigate to and within websites by using voice
¨ Talking dictionaries that speak definitions
In these S/GUI applications, tasks can
¨ Be completed using speech only where users issue a speech command or listen to the software speak to the software speak to them
¨ Rely on visual or manual gui aspects for example viewing a graphic or clicking a hyperlink
¨ Require or at least allow a combination of both a GUI
Non-speech audio
Some interface elements include audio but not speech these interface elements include music and sounds.some non speech audio is included in almost all interfaces of any type including S/GUI , AUI,and GUIs .examples of non speech audio include
¨ The computer beeps when the user makes an error
¨ The user clicks on a map and hears a low tone to indicate that the water to be foudna t that site is deep in the ground or a high tone to indicate that the water is closer to the surface
This is taken from the book "Designing Effective Speech Interfaces" by Susan Weinschenk and Dean T Barker
Thursday, October 26, 2006
Prototype- First Prototype
Ok, the first prototype is finally coded and is ready.

I am uploading a video at
www.freewebs.com/ruchiraparihar/proto_upload.htm
Wednesday, October 25, 2006
Thought Process - Frustration
Trying to visualize speech in some way.. and what the code is doing is not the way I want it to look on the screen.
Spent my day revising Visual Basic so that to incorporate Microsoft's speech recognition in it and to be able to save files real time..
The book I am reading is Mastering VB 6, what I have on my system is Visual Studio 2005, this so called upgraded version lacks in upward compatibility of the look and feel or atleast the terminology of the older version.Finding it really difficult to work for me.
Tried uninstalling VS2005, and tried installing VB 6, it did not happen because the system was able to find a dll which was of a higher version and hence could not be re-written and hence the set up was aborted.
So I installed Visual Studio 2005 again to work.. and now, Microsoft Office is having some problem with VS 2005, every time I try to open any Microsoft Office Application, it tries to install some of the missing components ( God Only Knows, where they went ) and the application either starts after a long delay or crashes.
So, this explains, that even if you have everything in your mind-all concepts ready-you are late or unable to implement- because the world is SOFT..
But in the end we are all dependent on softwares..
Tuesday, October 24, 2006
Explorations- Echo
Coding: Microphone properties in Flash 8
public class Microphone
extends Object
The Microphone class lets you capture audio from a microphone attached to the computer that is running Flash Player.
The Microphone class is primarily for use with Flash Communication Server but can be used in a limited fashion without the server, for example, to transmit sound from your microphone through the speakers on your local system.
Caution: Flash Player displays a Privacy dialog box that lets the user choose whether to allow or deny access to the microphone. Make sure your Stage size is at least 215 x 138 pixels; this is the minimum size Flash requires to display the dialog box.
Users and Administrative users may also disable microphone access on a per-site or global basis.
To create or reference a Microphone object, use the Microphone.get() method.
Availability: ActionScript 1.0; Flash Player 6
Property summary
activityLevel:Number [read-only]
A numeric value that specifies the amount of sound the microphone is detecting.
gain:Number [read-only]
The amount by which the microphone boosts the signal.
index:Number [read-only]
A zero-based integer that specifies the index of the microphone, as reflected in the array returned by Microphone.names.
muted:Boolean [read-only]
A Boolean value that specifies whether the user has denied access to the microphone (true) or allowed access (false).
name:String [read-only]
A string that specifies the name of the current sound capture device, as returned by the sound capture hardware.
static
names:Array [read-only]
Retrieves an array of strings reflecting the names of all available sound capture devices without displaying the Flash Player Privacy Settings panel.
rate:Number [read-only]
The rate at which the microphone is capturing sound, in kHz.
silenceLevel:Number [read-only]
An integer that specifies the amount of sound required to activate the microphone and invoke Microphone.onActivity(true).
silenceTimeOut:Number [read-only]
A numeric value representing the number of milliseconds between the time the microphone stops detecting sound and the time Microphone.onActivity(false) is invoked.
useEchoSuppression:Boolean [read-only]
Property (read-only); a Boolean value of true if echo suppression is enabled, false otherwise.
Event summary
Event
Description
onActivity = function(active:Boolean) {}
Invoked when the microphone starts or stops detecting sound.
onStatus = function(infoObject:Object) {}
Invoked when the user allows or denies access to the microphone.
Method summary
Modifiers
Signature
Description
static
get([index:Number]) : Microphone
Returns a reference to a Microphone object for capturing audio.
setGain(gain:Number) : Void
Sets the microphone gain--that is, the amount by which the microphone should multiply the signal before transmitting it.
setRate(rate:Number) : Void
Sets the rate, in kHz, at which the microphone should capture sound.
setSilenceLevel(silenceLevel:Number, [timeOut:Number]) : Void
Sets the minimum input level that should be considered sound and (optionally) the amount of silent time signifying that silence has actually begun.
setUseEchoSuppression(useEchoSuppression:Boolean) : Void
Specifies whether to use the echo suppression feature of the audio codec.
Methods inherited from class Object
-------
This makes it clear that if I use Flash Professional 8 for coding, i would be able to make use of the following properties of sound:
activityLevel, gain index,muted,name, rate and silenceLevel .
Monday, October 23, 2006
Thought Process - Intermediate state
I have been able to speech to text conversion. but have not been able to integrate it with some interface so that its output can be used as input
The project "white paper" is continuing.
At the same time I am trying to work on a script which would let people do graffiti online and save it.
Friday, October 20, 2006
Explorations - White Paper
The project “White Paper” is a part of the analytical study through implementation and experimentation for my classroom project “graffi-V”
The project is about collaboratively doing graffiti art on a big display by giving voice inputs. Whatever a person speaks, is broken down into different parameters of sound, i.e. frequency, loudness etc, and all these parameters are mapped to the different properties of the text ( which is speech to text converted from whatever the person has spoken ) like colour, font, font size etc. It is a project about sociability where people come together to collaboratively do graffiti on a display screen.
As a part of this project and to understand people’s behavior, I stuck three large white sheets in 3 Computer Laboratories of the campus. And left it with them in their labs for 3 days and allowed them to write their mind on them.

The initial observations are:
For such a thing to take place, the instrument with which they write is a major factor which holds them from writing, i.e. if people don’t have a pen in their hand ( or in the vicinity ) they wont attempt to write even if they have something to write
Very few people take the initiative to be the first ones to write, i.e. the initialization should be done already for people to carry on the chain reaction.
Usual scribbles on the white paper are often answering the one who has written before them.
This makes me think, if graffi-V should be a “one at a time” input system.
I will write down other observations as the days will pass by
Wednesday, October 18, 2006
Scenario
This is section covers scenarios,you need to understand the concept, in order to understand the scenarios:
I will include scenarios both during ideation and after conceptualization.
Scenarios during ideation are:

This was an intial scenario where what you sing is visualized.
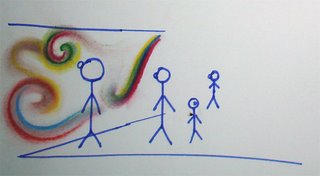
Then came the idea of drawing with sound.
Concept
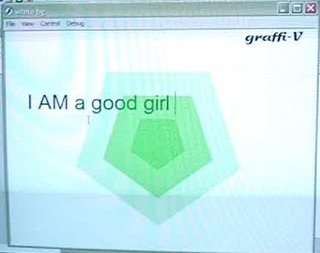
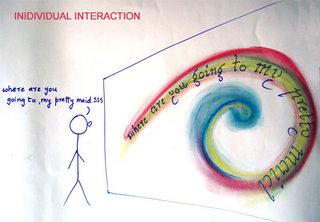
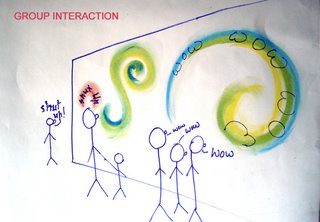
Graffi-V is experiential graffiti for creators and audience. A system enables the creators to create graffiti real time with whatever they are speaking.
Graffiti has been recognized as a powerful yet subtle form of expression. Collaborative Graffiti fulfills participants’ satisfaction on both desires for creation and social interaction. It lets them vent their emotions and also to leave a trail of memory behind.
The graffi-V creators will be able to create forms by merely speaking, and whatever they will be speaking will be displayed on the screen(text and form) according to the way they speak
Environmental Requirements:
- An otherwise silent place, where saying something "aloud" is "allowed"
- People
System Requirements:
- Microphone
- Display Screen
- Microsoft speech recognition engine
Implementation
- Cascaded style sheets
- xml
- Visual basic
- Flash 8 professional
Why Graffi-“V”
Graffi-V, V as Vocal,Visual and V as in We i.e. collaborative
It gives people a sense of connectedness with the environment.
Taking it forward..
It would be very nice if the audience would be able to hear how a particular line was spoken ..
if there is an inverse of this application which converts the patterns and text to voice,it would be great
Scenarios are covered in a later section.
Thought Process
Frustration of coding
Intermediate state
Graffiti :a thought
Properties of sound
Voice Recognition
Speech recongition on my system
Action and Reaction
Research
Research- Types of interfaces
Research - City Space
Graffiti as collaborative art
All about graffiti
Digital sound modelling
Experiments with some properties of sound
Robo responding to voice commands
Voice based Gaming
A Sound frequency dependent blender XP
Voice Input in Windows XP
Interactive Mirror
Wooden Mirror
Tuesday, October 17, 2006
Coding: Macromedia Communication Server 1.5
Uniting Communications and Applications
Develop the next generation of online communications: Deliver multi-way audio, video, and real-time data in your websites and Rich Internet Applications. Create engaging pre-sales applications that integrate audio, video, text, chat, and enterprise data. Develop powerful corporate presentations with streaming video and synchronized multimedia content that are deployed seamlessly within the context and branding of your site. Or build collaborative meeting applications that bring people together in real-time-connecting them to each other, to live data sources, and to back-end services for a significantly more compelling online experience.
* Powerful
* Easy
* Open
Powerful
Create and deploy powerful new communications functionality within your Internet applications-all delivered through the ubiquitous Macromedia Flash Player.
Add interactive functionality, including video and data broadcasts, shared whiteboards, virtual conference rooms, message boards, polling, live chat, messaging, and much more.
Deliver engaging real-time streamed media. Synchronize video streams with multimedia material to provide powerful supporting content for presentations. Use server scripting to control streams and program broadcasts to exact specifications. Provide end users with the best possible experience through a seamlessly integrated client that lets you brand your broadcast the way you want.
Tap into multi-way, multi-user communications for rich media messaging. Create and deploy rich media messaging features such as live video, audio or text-based messaging, chat, polling, and more. Support for both real-time and recorded messages makes a powerful base for developing compelling Internet communications.
Offer real-time collaboration. With team message boards, shared whiteboards, online conference rooms, and more, it's now easy for multiple connected users to share data and user interfaces in real-time. Create robust applications that can be used offline and synchronized automatically when the user returns online.
Easy
Rapidly develop rich communications applications with a highly integrated set of authoring, debugging, and administration tools.
Ensure the broadest reach for your work by deploying to the highly integrated and widely distributed Macromedia Flash Player. With Macromedia Flash Player, playback is consistent and reliable across browsers, platforms, and devices. Now you can deliver a completely customized experience with no unwanted offers, advertisements, outside branding, or new browsers launching to carry visitors away from your site.
Develop rich communications easily by leveraging existing skills and toolsets with the highly integrated Macromedia Studio MX. Easily add communications functionality within the Macromedia Flash MX authoring environment, using standards-based ActionScript. Take advantage of server-side ActionScript development in Macromedia Dreamweaver MX.
Take advantage of pre-built components to add streaming video, live chat, meeting rooms, instant messaging, and more to applications. It's as quick-and easy-as dragging and dropping communications features into place with Macromedia Flash MX. Use the library of components available for Macromedia Flash Communication Server MX, or build your own reusable components in the Macromedia Flash MX authoring environment.
Customize your communications solutions in a flexible, server-scripting environment that makes it easy to build communications solutions to meet specific project requirements.
Open
Macromedia Flash Communication Server MX works with major existing platforms on the client and server, so you can enhance and leverage your existing investments.
Integrate seamlessly with application servers. Use built-in support for Flash Remoting to connect to application servers, databases, XML web services, and directory services, enabling integration with existing applications and data-and providing real-time data for customers. Flash Remoting is native in Macromedia ColdFusion and JRun and available separately for .NET and J2EE.
Provide a simpler experience for your users. Macromedia Flash Player automatically recognizes installed microphones and standard USB or Firewire cameras, so your users can begin communicating immediately-without performing complex installations or configurations.
Rely on a familiar scripting model. Create compelling applications with just a few lines of code. Use standard JavaScript scripting language (ECMA-262) to build application logic on the server.
Research - City Space
Director: Craig Noble
It is tried to uncover a world where the line between art and vandalism is blurred.creative expression and social responsiblity meet head on in an articulate collage of fact and opinion as subculture and bureaucracy collide.
the paper is worth reading, it changes one's perspective towards art and vandalism..
Saturday, October 14, 2006
Research-Collaborative art
It's all about finding social empowerment through the spirit of collaboration. The process of working together helps the participants build bridges to each other, and leads to the creation of high-calibre art.
Common Weal inspires ideas for social change through art. By linking professional artists with communities to engage in collaborative art projects, we empower people - and their communities - to tell their stories in their own voices.
Research- WIFI Graffiti ( Wiffiti )
http://www.wiffiti.com/txtoutloud/
A new technology called Wiffiti is,enabling people to send text messages to large flat panel displays in social venues such as cafes, bars and clubs. Wiffiti is grounded upon the premise that sending messages to a public screen rather than a private phone will resonate with both the location and its community.

Messages sent to Wiffiti screens are also visible on this web site, encouraging people to watch “the word on the street” as it unfolds. Click on the viewer tab, pick a screen, and send a txt from anywhere. Then, sit back and watch responses appear from across the country! Better yet, head over to the closest Wiffiti location to txt out loud!
The first Wiffiti screen was installed in January 2006 at Someday Café in Boston, MA, a city that now has three other Wiffiti screens. Screens are now spreading rapidly, appearing in Chicago, Denver, Seattle, Knoxville, Boulder and New York.
I tried getting a password and also tried to log in, but it does not work for international audience.
Thursday, October 12, 2006
Research- Graffiti
The word "graffiti" derives from the Greek word graphein meaning: to write. This evolved into the Latin word graffito. Graffiti is the plural form of graffito. Simply put, graffiti is a drawing, scribbling or writing on a flat surface. Today, we equate graffiti with the "New York" or "Hip Hop" style which emerged from New York City in the 1970's.
Graffiti Culture
Graffiti quickly became a social scene. Friends often form crews of vandals. One early crew wrote TAG as their crew name, an acronym for Tuff Artists Group. Tag has since come to mean both graffiti writing, 'tagging' and graffiti, a 'tag'. Crews often tag together, writing both the crew tag and their own personal tags. Graffiti has its own language with terms such as: piece, toy, wild-style, and racking.
Graffiti Tools
At first pens and markers were used, but these were limited as to what types of surfaces they worked on so very quickly everyone was using spray paint. Spray paint could mark all types of surfaces and was quick and easy to use. The spray nozzles on the spray cans proved inadequate to create the more colorful pieces. Caps from deodorant, insecticide, WD-40 and other aerosol cans were substituted to allow for a finer or thicker stream of paint. As municipalities began passing graffiti ordinances outlawing graffiti implements, clever ways of disguising paint implements were devised. Shoe polish, deodorant roll-ons and other seemingly innocent containers are emptied and filled with paint. Markers, art pens and grease pens obtained from art supply stores are also used. In fact nearly any object which can leave a mark on most surfaces are used by taggers, though the spray can is the medium of choice for most taggers.
Graffiti in the 21st Century
As graffiti has grown, so too has its character. What began as an urban lower-income protest, nationally, graffiti now spans all racial and economic groups. While many inner-city kids are still heavily involved in the graffiti culture, one tagger recently caught in Philadelphia was a 27 year old stockbroker who drove to tagging sites in his BMW. Styles have dramatically evolved from the simple cursory style, which is still the most prevalent, to intricate interlocking letter graphic designs with multiple colors called pieces (from masterpieces).
Graffiti Style Art
While most taggers are simply interested in seeing their name in as many places as possible and as visibly as possible, some taggers are more contented to find secluded warehouse walls where they can practice their pieces. Some of these taggers are able to sell twelve foot canvases of their work for upwards of 10 - 12 thousand dollars.
Commercialization, the Web and the World
Graffiti shops, both retail and on-line, sell a wide variety of items to taggers. Caps, markers, magazines, T-shirts, backpacks, shorts with hidden pockets, even drawing books with templates of different railroad cars can be purchased. Over 25,000 graffiti sites exist on the world wide web, the majority of these are pro-graffiti. Graffiti vandalism is a problem in nearly every urban area in the world. Pro-graffiti web sites post photos of graffiti from Europe, South America, the Philippines, Australia, South Africa, China and Japan. Billions of dollars worldwide are spent each year in an effort to curb graffiti
one such site i found was,a graffiti creator http://www.graffiticreator.net/ where you can (online) create text images like graffiti
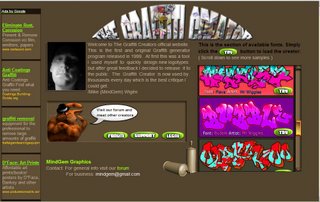
tried writing my name:

Thought Process - Graffiti: a thought

I think graffiti is a way of expressing oneself through the medium of wall and paint.
It is a way to leave memory trails behind so that one who comes after you can see what you have done.It is a form of art and is liked very much.It can also be a method of communication.I think that advertisements and even election campaigns make use of graffiti.It can sometimes be criminal or done as vandalism.
Wednesday, October 11, 2006
Research-Digital Sound Modelling
Human sound perception varies, probably even more than human vision. Basic sound modelling techniques need to work well for a large proportion of people with "normal" hearing. Here are typical parameters of human hearing, based on my interpretation of information in Audition, by Pierre Buser and Michel Imbert, English translation by R. H. Kay, MIT Press, Cambridge MA, 1992, and in the notes to the CD Audio Demonstrations, by A. J. M. Houtsma, T. D. Rossing, W. M. Wagenaars, Philips 1126-061.
Frequency range:
20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Musically, that is a spread of about 10 octaves (the piano has about 7 octaves). Some people hear signals with frequencies well above 20,000 Hz. In a changing sound, frequency components far above 20,000 Hz may have perceptible effects, even though they are not noticeable as components of the sound.
Frequency discrimination:
Between about 1,000 Hz and 8,000 Hz, we notice changes between frequencies whose ratios are about 1.002 or 1.003, which is roughly 200 to 350 steps per octave, or something between 1/30 and 1/15 of a musical half step. Outside of this range, discrimination is poorer, but for most of the range of audible frequencies we notice changes in ratios smaller than 1.01, which gives more than 60 steps per octave, or something smaller than 1/5 of a half step. Discrimination of frequencies played in sequence is bit less---typically about 90 steps per octave or about 1/8 of a half step.
Musicians interested in nonstandard pitches have usually used the cent, which is 1/100 of a half step, or the savart, which is 1/25 of a half step. In complex sounds, frequency distinctions may be important even though they are less than those preceptible as changes in a simple helical signal. There is also a unit, called the mel that is like a pitch measurement, but scaled to the people's judgments that certain pitches are ``twice as high'' as others in psychological experiments. Although it is defined in terms of perceptual parameters, the mel probably does not correspond as well to perception as the various musical measures.
Taking frequency resolution between 90 and 360 steps per octave, over a range of 10 octaves, we get 900 to 3,600 distinguishable frequencies. But, it seems that we cannot exploit those as independent bits, and the practical information capacity of a single sound is much less.
Critical bands:
Our hearing is affected by "critical bands" of frequencies. The width of these bands is about 1/3 octave, but it varies according to the center frequency. The bands are not discrete, rather there is a critical band at each center frequency. Frequency discrimination for signals of only one wavelength is approximately the width of a critical band. A sound is perceived louder if its energy is spread across many critical bands, rather than concentrated in a few. I think that critical bands represent the basic frequency resolution of the filters in the cochlea. Greater frequency discrimination presumably comes from further filtering in the nervous system. So, about 30 critical bands cover the 10 octaves of human frequency perception, yielding 30 disjoint bands. But, it is not at all clear to me that a single mix of frequencies can present even 30 bits to our brains in a usable way.
Beat frequencies:
When two helical signals are played simultaneously with frequencies differing by 2-3 Hz, we hear a single intermediate frequency, getting louder and softer. This phenomenon is called "beats." The rate of the beats is is the difference between the helical frequencies. Beats may be heard with frequency differences as high as 35 Hz, but the boundary is extremely fuzzy.
Event resolution:
I haven't found data on this point yet. I am pretty confident that I can distinguish clicks separated by 1/30 second, and I believe that I can go close to 1/100 second. Event resolution depends crucially on the frequency components of the events. The start of a helical signal at frequency F cannot be perceived more precisely than about 1/F.
Transient scale:
Again, no data yet. I think that transients occur on a scale of 1/1000s to 1/100s of a second.
Measuring loudness:
I found the complications of different ways of measuring loudness quite confusing, and haven't succeeded in reducing them to a brief description. Loudness can be related either to power level, typically measured in Watts per square meter (W/m^2), or to change in pressure, typically measured in bars, where 1 bar is the normal pressure of the atmosphere. In either case logarithmic units called decibels (dB) are used, where a difference of 10 dB represents multiplying the power by 10, a difference of 20 dB represents multiplying the pressure by 10 (power is proportional to the square of pressure). You will find different choices for the 0 of the decibel scale. A typical choice is that 0 dB is about 2/10^10 bars, or 1/10^12 Watts per square meter. On this scale, typical loudness measures include
• 10 dB rustling leaves
• 20 dB noise in a recording studio
• 30 dB noise in a quiet room
• 30-70 dB conversational speech
• 40 dB noise on a quiet street
• 50 dB quiet music
• 60 dB cocktail party conversation
• 70-80 dB noisy street
• 90 dB symphony orchestra, playing loud
• 100 dB jackhammer at 2 meters
• 120 dB thunder, or jet engine at 10 meters
There is a special unit of loudness, called the sone, that is scaled to our auditory sensitivity at different frequencies. In principle, this is a good idea, but the extra complication is probably not worth it for most of our purposes.
Loudness range:
From about 500 Hz to 2000 Hz we detect sounds as quiet as 5 dB, which is about 4/10^10 bar pressure change, or 3/10^12 Watts per square meter. At lower frequencies, sensitivity reduces, and we need about 75 dB to hear a sound at 20 Hz. At higher frequencies the curve is more complicated, improving to about -4 dB at 4000 Hz, then varying up to about 25 dB at 12000 Hz. There is no fixed upper limit to detectible sound. Around 100 dB (2/10^5 bar, 1/10^2 Watts per square meter) sound gets to be uncomfortably loud. Around 140 dB (2/10^2 bar, 10^2 Watts per square meter) it becomes physically painful. Eventually, I suppose it becomes lethal. The power ratio between the softest detectable sound and the loudest usable sound is something like 10^4 to 10^10, a range of 40-100 dB.
Loudness discrimination:
Minimum noticeable changes in loudness vary from about 0.15 dB to about 10 dB, depending on the type of signal. 3/4 dB to 1 dB is probably a practical increment. Loudness is a tricky parameter for carrying information, since our perception of it is very sensitive to context, and we have poor memory for loudness levels. 3/4 to 1 dB discrimination, over a 60 dB range, suggests 45-60 discriminable loudness levels. Since a given sound has only one loudness, this suggests that loudness can only carry log 45 to log 60 (base 2), that is 5 or 6 bits of information. That is probably more than can be used practically. It's not at all clear how well relative loudness of different components of a sound can be distinguished. In strictly monaural sound, we probably shouldn't expect to distinguish more than one loudness value per critical band, or 30 in all, with a total capacity of 150-180 bits. But, the threshhold of pain is probably determined more by the total loudness than by the maximum loudness per critical band, and other perceptual complications probably restrict the total information capacity of the loudness channel to something much smaller.
Tuesday, October 10, 2006
Thought Process - Sound and Its properties

A general thought on properties of sound which can be made use of. I still don’t know how many of these properties I will be able to filter and separate out to be mapped to the different elements of text. But I think if these properties exist , there must definitely be a way of separating them and making use of them.
Sunday, October 08, 2006
Research -Sound Experiments
Visualising the sound waves through the flames.. interesting
Normal media players like winamp and windows media player also have visualizations which are generated by studying sound,
I think this one is a similar experiment
Visualization experiment
Resonance Effect
How sound frequencies and their resonating effect can generate patterns
Messa di Voce:
Strange sound interactions.. visualizations as well.
This is an installation in public space..
See for yourself..
Saturday, October 07, 2006
Research -Voice Recognition and Control
Thought that it was some speech recognition integrated with flash.Actually I am thinking to do it this way.. planning for a collaborative social way of interacting with a medium through voice and sound based inputs..
but this turned out to be how speech recognition can used in flash to invoke commands.Sad..
Voice control
This shows how a robot is controlled based on voice inputs.
Friday, October 06, 2006
Research & Thought Process -Voice recogntion
I found this very interesting sound based interaction on YOUTUBE .It was one of my concepts, of gaming with voice based signals, here through speech recognition , different events are triggered and interactions happen.
Its interesting to watch and I think should be even more interesting to play with.
This is voice based inputs for a game.
What I am thinking is a simpler version where a user through sound inputs can trigger something, a simple game like Mario for example, where the basic action is to jump (if we keep the moving forward as constant)..
those single click games..
simple thing like to keep running to win the race..
I also have thought about a scenario where a group of people can play a racing game, the screen shows a corresponding car, and the speech recongnition system recongnizes each sound input and accordingly triggers the cars to move forward.. the louder you shout, or the more consistantly you shout, the more will be your speed.And hence a game can be played collaboratively.

God Help Their Neighbours!!
Wednesday, October 04, 2006
Thought Process-Voice Recognition on my PC
I have installed Microsoft speech recognition on my computer and I did train my computer to understand what I say for some 1.5 Hrs and then it could partly understand what I was saying.By the above statement I mean that I installed the speech recognition engine and voice trained it for microsoft word, so that I could dictate text to it.It is fascinating to see it work.But when I ask someone else to give a dictation what it types is garbage.
It also understands commands in the command mode.I can save and open and edit files.
I will have to think how to convert these text files into some other form in real time.I will have to script something I think...
Let's see.
Research- voice recognition in machines
Just watch this video, its amazing, it shows how with the change in the loudness of sound , the speed of the blender increases... its also very funny... and scary also , because this blender is supposed to have a mood of its own and it suddenly starts on its own sometimes!
Tuesday, October 03, 2006
Research - Windows did it again!
Found this interesting video of how Windows Vista recognizes speech inputs and executes commands.. though its kinda funny how he says "double click 'folder_name' " but its nice to see it work.I liked the way he marks the points in MSPAINT..
This speech recognition feature was first introduced with microsoft office XP, and now it is encapsulated with the operating system!
Monday, October 02, 2006
Thought Process-Action and Reaction
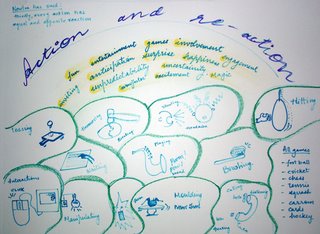
Analysing some tasks in daily life:
Tossing a ball
Clicking a mouse button
Shouting
Playing an instrument
Talking on the phone
Bursting a cracker
Moulding a pot
Switching on a switch
Hitting a punching bag
each one of the above mentioned activities have the
basic "Action-Reaction" sequences
Now, these things can be more exciting if they have
a factor each of:
-fun
-entertainment
-game
-involvement
-inviting
-anticipation
-surprise
-engagement
-uncertainty
-"wow"
-magic
-unpredictability
Friday, September 08, 2006
Intermission
Working for the ergonomics assignment..
i shall be back soon..
I know I have lots to do..
Brainstorming at the second level
and its high time to think finally of finalizing what I am doing..
and hence the big question is, what I am going to do with sound..
Here are some Ideas:

Randomly thinking what the word sound generates in the mind and writing them all down on the paper.
I want the output of this project to be a fun-filled experience , which should be a taking a break kind of thing.We know that sound is one of the major sense inputs that we are taking in.
One can think of taste, imagery or textures associated with sound
Kaleidoscope of sound, this can be an interesting thing as the echo is..
If it is echo, it can be an echo in a different way
-echo of opposite words,
-echo of similar words,
-images as echo!
-what if there is am interface where you see lots of flowers and butterflies, and you shout and they all go away.. you keep silent and they come back and sit down..
-what about 3D visualizations of sound..
I want this to be experiential, inviting, tempting, anticipating.. having all those factors, which make things interesting and enjoyable..
It can find a place in amusement parks, public spaces where people meet, parks, gully markets like palika bazar,and exhibition spaces.
Saturday, September 02, 2006
Research -Interactive Mirrors
Interestingly done, almost an immersive environment.. check the link http://www.interactivemirror.net/
here is some of the matter from there.
They also have a video on the website, which can be checked.

The objective was to create a unique and fascinating interactive experience, engaging consumers at larger-than-life size and immersing them in the presentation. The interactive mirror shares the brand’s philosophy of using design to create a more emotionally rich experience and demonstrates how design is manifest in Infiniti vehicles.
The installation consists of three 8’ high by 3.5 ’ wide panes of mirrored glass placed side by side, each displaying rear-projected content from a high-lumen projector. A user standing in front of the mirrors has the unusual sensation of seeing their reflection and the projected content simultaneously.
Sensors embedded in the structure above each pane register when a user reaches out to a “hot spot,” allowing users to navigate the projected content without ever needing to touch the “screen” or press a “button.” This combined with scale of the system, and the projected image being captured on the inside surface of the glass creates a unique spatial experience where the content appears organically before the viewer. An additional sensor recognizes when a user approaches and automatically activates the mirror to welcome the visitor.
To take advantage of the spatial experience, content was designed in three dimensions, using scale, motion and depth perspective to make the user feel like she is immersed in and moving through the communication, not merely viewing it. Integrating full motion video, Flash animation, motion graphics, still photography, dynamic type and responsive sound, the content enables users to explore the guiding vision of the brand. This includes a broad sampling of ways this vision has transformed how Infiniti vehicles look, feel and move, as well as how each Infiniti model is an expression of the brand promise.
Creation of the Infiniti Interactive Mirrors and their content was a collaborative effort. The George P. Johnson Company along with Nikolai Cornell of madein.la developed the exhibit and the technology concept. Phil van Allen of Commotion New Media designed, developed and integrated the sensor system. The Designory directed, designed and wrote the content. And Mindflood was responsible for motion graphics design as well as video integration and user-interface programming for the Flash platform.
Friday, September 01, 2006
Research -Wooden Mirror
| A very clever mechanical wooden mirror. "The 4 mechanical mirrors are made of various materials but share the same behavior and interaction; any person standing in front of one of these pieces is instantly reflected on its surface. The mechanical mirrors all have video cameras, motors and computers on board and produce a soothing sound as the viewer interacts with them. " | |
Wednesday, August 30, 2006
Ideation
This is a quick view ( or you may call it a sneak peak) to the process of
ideation I followed.
Brainstorming for the ideas:

I had 3 Initial Ideas in the beginning, which were

I decided to take up sound as my final medium

Brainstormed more on sound, and thought of possible variations
Generally observed action and reaction in daily life and got inspired and
also thought of adding a magical element to it.
Thought about graffiti with sound, and hence brainstormed on graffiti.
Friday, August 18, 2006
The final three

I think I will have to choose from these three ideas,
first one being, creating theme amusement parks, or places where "out of aged" fun loving people can go and enjoye rides, swings and slides..
second one is interactive mirrors, every time you look into the mirror , you see something new along with your own image
third one being sounds and echoes, something with sound..
lets see..
Wednesday, August 16, 2006
Coming back..
So this time I took to think about the various new media things which can be done.
Basically thinking about the media which are possible..

So.. firstly I thought of by what all means do we sense, the five sense organs, and the way we perceive.Re-considering the objective, trying to understand what am I trying to focus at..
I have some three ideas, fist is an amusement park, for the "over aged" ones, second is interactive mirrors, and third one is something with audio textures.
From the next week, we are to start with "Design for the web", I will think if this project can be taken up there and continued with that course, or if not, then later.
Saturday, August 12, 2006
Brainstorming
This is how we start with any project.Imagine to sart a project with
as brief a brief as "anything new media".
hmm.. I spent the whole of my week thinking about what all things I
have ever thought of..
all my concepts which I have had throughout my life as a student here,
and try to pick up anything which interests me, which I would love to
carry forward as a classroom project.
So here is a list of some of my ideas:
An electronic newspaper, which you purchase once and keep with you forever, it gets wireless feeds of news from the news service you want to subscribe to , and hence you dont have to pay for a newspaper everyday.Make it interactive and you can choose what you want.A single page can serve as a complete paper.BUT.. ahem.. you cant wrap your chappals in it!
A New Media dustbin, which becomes aware of the people around it and tells them to throw the waste in it, hence stopping them to litter.
Or have plates and bottles ( use and throw kinds ) which remind the user to throw them into the dust bin.
Next was immersive theatres, whatever the scene on the screen is, the side walls , and the ceiling of the theater also turn to that form and colour, so that it gives the user a totally immersive feeling,may be even the temperature can be generated according to the colours on the screen..
An experiential design for the people who are over-age for swings in parks, creating a feeling of sitting in a merry go round, or see-saw, or swing etc.
Still thinking on what to do..
I think I need to think more...
Thursday, August 10, 2006
Why this blog..
As the discipline name goes, which is New Media, the course brief was to make something which is New..
New Media is perceived as a medium which is anticipated to come next.We as New Media Designers are supposed to have a foresight of what is going to come next in any field.
Usually at any design school of the world , the design disciplines are usually categorised as ID (industrial design) and VC ( visual communication ), but NEW MEDIA is an interesting mix of both the tangibles and the intangibles.. it also has a major component of technology (which is more of computers and information technology now-a-days).
So, that gives a brief idea of what the discipline is about and what is expected from the students.
As the design project of the third semester we have to come up with a concept and prototype it.. ( also implement it ) of possible.
as per the time-table, the project which is apparently of a total course duration of 9 weeks started in the 7th week of the semester , which is the first week of august
AND TODAY IS THE DAY WHEN I AM STARTING TO DOCUMENT ALL WHAT I HAVE DONE TILL NOW AND I THINK THAT THIS BLOG CAN HELP ME DOCUMENT IT PROPERLY AND WITHOUT CLUTTER.
